Entertainment
Entertainment occupies a substantial portion of Americans’ leisure time and thus shapes behaviors for hours of every day. For this industry, we examined products and services in three categories: 1) social media platforms; 2) video game platforms and publishing; and 3) video streaming services.
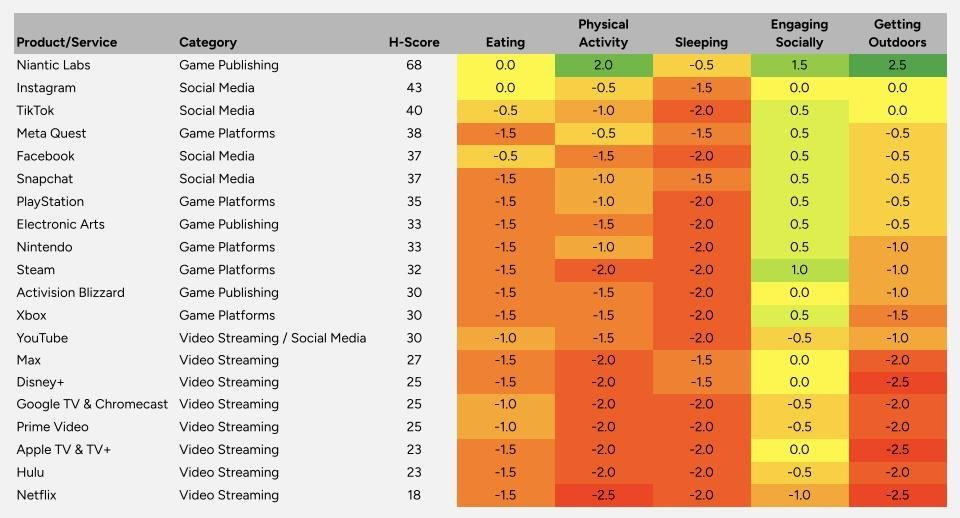
Overall Ratings
Highlights
The results across all three categories were almost uniformly negative. With one exception (Niantic Labs), entertainment products and services scored poorly on their influences on eating, physical activity, sleeping and getting outdoors. Scores for engaging socially varied, but, where they were positive, were only modestly so. The poor results stem largely from the nature of the dominant forms of entertainment, which are typically consumed indoors, in a sedentary fashion and are essentially available 24/7.
Social Media Platforms
Highlights and Opportunities
We reviewed five social media platforms: Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, TikTok and YouTube (which mixes elements of social media with video streaming). All scored in net negative territory, although, generally speaking, they were rated higher than the video game platforms and publishers and video streaming services. The influence of the social media platforms on health is complex, with evidence pointing to both positive and negative influences for most behaviors and contradictions between user reports of behaviors and perceptions of influences on those behaviors. (For example, many users of social media reported unhealthy eating habits like higher consumption of fast food, yet also reported neutral or positive influences of social media on their diets). The platforms scored worst on sleep, despite several of them offering bedtime reminders or other time controls, which our research found to be of limited value.
Due to the complexity of the influences, it is important for the platforms to research their influences on users’ health habits, particularly with respect to diet, sleep and social engagement to understand where they need to adapt. Other opportunities lie in establishing a robust bedtime mode and giving users more agency by helping them define their preferences for how much they wish to spend on those platforms and then supporting their choices.
Methodology
In addition to reviewing the scientific literature for studies that linked social media (either generally or the specific platforms individually), we relied heavily on the results of our original consumer survey that asked 3,000+ US adults about their social media use (including platform-specific data), their health habits and the links between them.(1) We also examined the features, designs and user experiences of each platform to understand how those designs contributed to overall time on the platforms and potentially influenced the different health behaviors.
Product Profiles
Video Game Platforms and Publishers
Highlights and Opportunities
We looked at the leading video game platform (or console) providers – Nintendo, PlayStation and Xbox – along with the online platform Steam and the virtual reality (VR) console Meta Quest. In addition, we reviewed the most popular games from two leading publishers – Activision Blizzard, known for its Call of Duty franchiser and Electronic Arts, which publishes popular sports titles FIFA, Madden NFL and adventure games like Apex Legends and the Star Wars franchise. We included Niantic Labs, the developer and publisher of mobile, augmented reality (AR) games like Pokémon GO, for contrast.
Niantic, whose approach, which draws players into outdoor, physical activity that is often very social, is markedly different from the more traditional console-based games, was in a league by itself. It scored highly on three behaviors, with only a concern about sleep. The leading platforms were all quite similar, scoring poorly on their influences on eating, physical activity, sleep and getting outdoors. The exception was Meta Quest, whose VR games were reported by users to be more likely to include physical activity. Poor scores relating to eating habits were largely driven by user reports of high fast food and energy drink consumption, along with greater use of food delivery services. Users of all platforms reported frequent deferring of sleep to continue game play.
A key driver of the poor ratings for most platforms and publishers is the impact that long (and frequent) gaming sessions have on crowding out healthy behaviors – with snacking, fast food and deferred sleep resulting. Key opportunities lie in working with users to moderate the amount of time spent on games, establishing robust bedtime modes and emphasizing multiplayer modes over single-player options. AR presents a significant opportunity to build games that draw people outside of their homes and entertain them in more physical, more social ways.
Methodology
As with social media, we supplemented a review of the scientific literature and examination of how the products function with data from our 2023 survey that delved into game play and related health habits.(2)
Product Profiles
Video Streaming Services
Highlights and Opportunities
Within the category of video streaming services, we looked at five of the leading programming providers: Disney+, Hulu, Max, Netflix, Prime Video and two hardware/software platforms: Apple TV (along with its programming subscription service Apple TV+) and Google TV (and its Chromecast device). We include YouTube in this category (as well as in the category of social media platforms) as it includes aspects of both video streaming and social media.
All services scored quite poorly – among the worst scores in the Index overall – in part because television watching is a typically indoor, sedentary activity that is associated with unheal;thy eating but also due to the design choices and features that push users to binge-watch. There were no standouts among the different services as there is remarkable consistency in the implementations across the industry.
The key opportunities are to help users manage their consumption by dialing back the binge-watching features (namely autoplay) and creating serious bedtime modes that would respect users’ intentions to sleep. While there has been some progress since our 2022 Index – users can now disable autoplay in most services – the industry can go farther.
Methodology
We reviewed the scientific literature on the associations of television watching and different health behaviors. We looked closely at how the products are designed, testing different features and implementations. We supplemented this information with original survey research, conducted in 2020, on video streaming use patterns and links to health behaviors.(3)
Product Profiles
Team
Research, analysis and writing by Alec McMorris, MPH (social media platforms), Lorena Moreno Aguilar and Evan Cook (video game platforms and publishing) and Steve Downs (video streaming services). Scientific review and consultation on influences and opportunities relating to social engagement by Julianne Holt-Lunstad, PhD, Carla Perissinotto, MD, MHS, Matthew Smith, PhD, MPH and Abigail Barth, MPH.
Notes
Alec McMorris. Measuring the Product Environment: How Does Social Media Influence Health Behaviors? Building H on Medium, May 1, 2024.
Evan Cook. Measuring the Product Environment: How do Video Games on Health Behaviors? Building H on Medium. April 23, 2024.
Carlo Martinez. A Survey of Modern Life: Entertainment. Building H on Medium. May 4, 2021.